Laparoscopic Surgery for Hernias: Advantages and Benefits
Hernias are a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. They occur when an organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. Traditionally, hernia repairs have been performed through open surgery, which involves a large incision and a longer recovery period. However, in recent years, laparoscopic surgery has gained popularity as a minimally invasive alternative for hernia repairs. In this blog post, we will explore the advantages and benefits of laparoscopic surgery for hernias.
Different Types of Laparoscopic Hernia Surgeries
Inguinal Hernia Repair
Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernias, occurring in the groin area. Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair is a highly effective and widely performed procedure. The surgeon makes a few small incisions near the hernia site and inserts the laparoscope to visualize the hernia defect. Specialized instruments are used to push the herniated tissue back into place and reinforce the weakened area with a mesh.
The mesh acts as a support structure to prevent future herniation. This minimally invasive approach results in less postoperative pain, faster recovery, and a lower risk of complications compared to open surgery. Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair is associated with a high success rate and a reduced risk of hernia recurrence.
Ventral and Incisional Hernia Repair
Ventral hernias occur when abdominal tissue protrudes through a weakness in the abdominal wall, often at the site of a previous surgical incision. Incisional hernias, a specific type of ventral hernia, develop at the site of a previous surgical incision. Laparoscopic ventral and incisional hernia repair involve the same principles as other laparoscopic hernia repairs. The surgeon creates small incisions near the hernia site, inserts the laparoscope, and repairs the hernia using mesh or sutures.
The advantage of laparoscopic surgery for ventral and incisional hernias is that it allows for a more precise repair and better visualization of the hernia defect, reducing the risk of complications and hernia recurrence. Additionally, the smaller incisions result in less postoperative pain, quicker recovery, and improved cosmetic outcomes.
Hiatal Hernia Repair
Hiatal hernias occur when the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. Laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat this condition. During the surgery, the surgeon makes small incisions in the abdominal area and inserts the laparoscope to access the hiatal hernia. The stomach is carefully repositioned below the diaphragm, and the diaphragmatic opening is repaired. In some cases, a mesh may be used to provide additional reinforcement.
Laparoscopic hiatal hernia repair offers several advantages, including reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery compared to open surgery. It also allows for improved visualization and precise repair, leading to a lower risk of complications and a decreased chance of hernia recurrence.
Advantages and Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Now that we have discussed the three types of laparoscopic hernia repair, let's take a look at some of the advantages and benefits associated with this minimally invasive technique.
Minimally Invasive Procedure
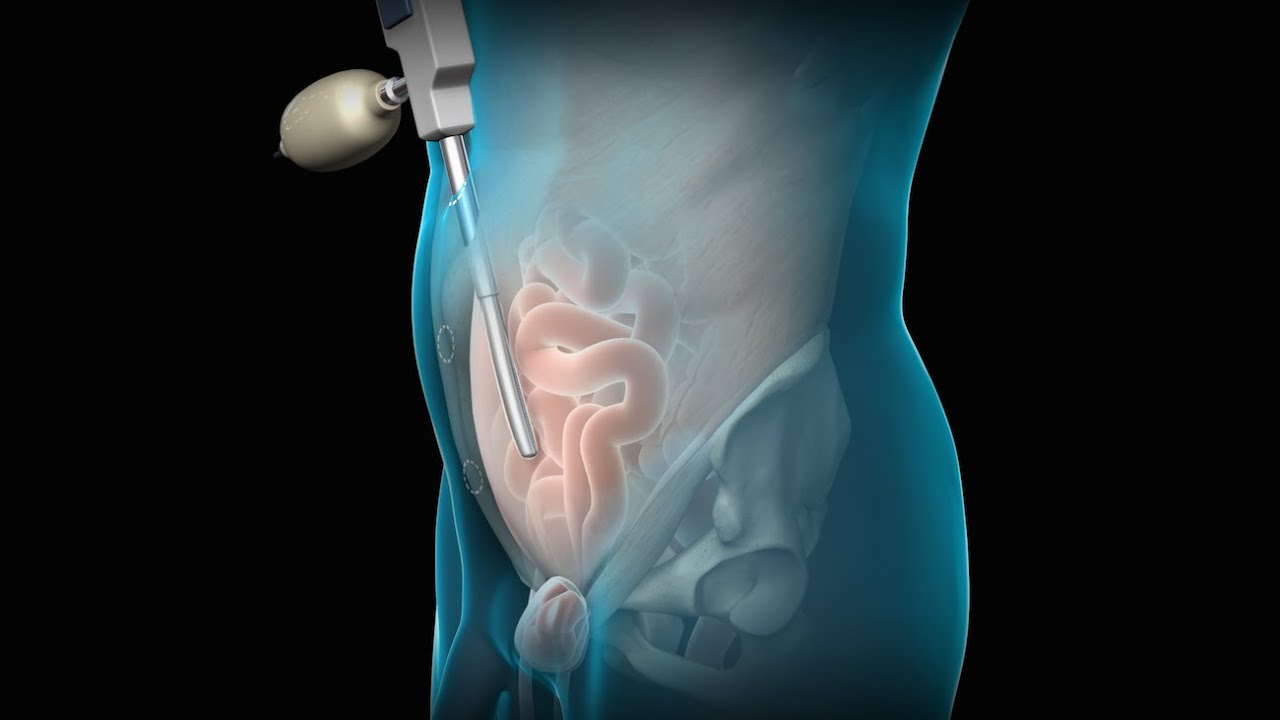
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, involves making several small incisions instead of one large incision. Through these small incisions, a laparoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) and specialized surgical instruments are inserted. The surgeon then performs the repair while viewing the internal organs on a monitor. Compared to open surgery, laparoscopic surgery offers several advantages.
Reduced Postoperative Pain
One significant benefit of laparoscopic hernia surgery is reduced postoperative pain. The smaller incisions and the use of specialized instruments allow for less tissue trauma during the procedure. This results in less pain and discomfort for the patient after surgery. Studies have shown that patients who undergo laparoscopic hernia repair experience less pain, require fewer pain medications, and have a quicker return to normal activities compared to those who undergo open surgery.
Faster Recovery and Shorter Hospital Stay
Due to the minimally invasive nature of laparoscopic hernia surgery, the recovery period is significantly shorter than that of open surgery. The smaller incisions result in less scarring and a lower risk of infection. Patients typically experience less postoperative discomfort and can resume their daily activities sooner. Moreover, laparoscopic surgery is usually performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to go home on the same day as the procedure, eliminating the need for an extended hospital stay.
Reduced Risk of Complications
Laparoscopic surgery for hernias carries a lower risk of complications compared to open surgery. The smaller incisions reduce the risk of wound infections, hernia recurrence, and other surgical site complications. Additionally, laparoscopic procedures provide better visualization of the hernia defect, allowing for more precise repair. This improved accuracy helps minimize the risk of damage to surrounding tissues and organs, leading to a safer surgical outcome.
Cosmetic Benefits
In addition to the medical advantages, laparoscopic hernia surgery offers cosmetic benefits as well. The smaller incisions used in laparoscopic procedures result in smaller scars, which are less noticeable and more aesthetically pleasing than the larger scars associated with open surgery. This can be particularly important for patients concerned about the cosmetic outcome of their procedure, especially when the hernia occurs in a visible area of the body.
Potential for Bilateral Repair
Laparoscopic surgery provides the advantage of bilateral repair, which means that both sides of a hernia can be addressed simultaneously during the same procedure. In contrast, open surgery often requires separate surgeries to repair hernias on both sides, leading to additional time and inconvenience for the patient. The bilateral laparoscopic repair offers the advantage of addressing multiple hernias in a more efficient and streamlined manner.
Lower Risk for Recurrence
One of the main concerns for hernia patients is the risk of recurrence. Studies have shown that laparoscopic hernia repair has a lower recurrence rate compared to open surgery. The laparoscopic approach allows for better tension-free mesh placement, reducing the risk of hernia recurrence. Additionally, the improved visualization provided by the laparoscope helps ensure a more thorough repair, decreasing the likelihood of future hernias.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery has revolutionized the field of hernia repair by offering numerous advantages and benefits over traditional open surgery. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure leads to reduced postoperative pain, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays. It also reduces the risk of complications and hernia recurrence. Furthermore, laparoscopic surgery provides cosmetic benefits, with smaller scars that are less noticeable. Overall, laparoscopic hernia surgery is an excellent option for patients seeking a safer, more efficient, and aesthetically pleasing solution for their hernia repair needs.

